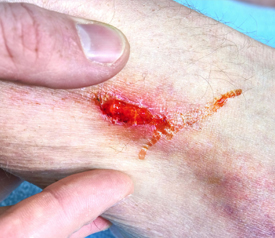
For the geriatric population (65 years and older) skin tears are a growing concern. It is estimated that almost 1/4 of the population will fall into this age category by 2060 making it an unavoidable truth that health care professionals will need to make skin tear prevention a priority in their care plan.
Skin tears are placed into three categories and based on whether the flap of skin is still repairable.
- Category 1: The torn skin has a flap that is healthy enough to close the edges. There is hope that with a light dressing that the wound will heal. Subcatagories for this type of wound include Category 1A (healthy pink flap of skin) and Category 1B in which the skin is bruised in appearance or pale and less likely to heal.
- Category 2: The skin flap is damaged and won’t close properly. In this case, the tear will not heal correctly because the flap won’t reach the edges of the wound. Like above, Category 2a means the flap is pink. Category 2b means the flap is pale or blue.
- Category 3: The skin flap is completely gone. This will take the longest to heal.
It is Important to Identify the Common Risk Factors the Lead to Skin Tears
The most common risk factors may include:
Advanced Age – With aging comes a measurable loss in dermal thickness. Elderly patients with thin skin often become bruised by bumping into things or by simply removing dressings. In more extreme cases the skin tears and the results can leave a wound that may become infected and lead to costly, long term treatments.
Dehydration and Dry Skin – Hydration and well moisturized skin will result in a healthy dermis and lead to less skin tears.
Nutrition and Vitamin Deficiencies – Malnutrition can lead to poor skin health. The layer of fat under the skin that normally acts as a cushion against bumps and pressure. If this cushion of fat disappears, an older person has a much higher risk of skin tears. It is important to maintain a diet rich in healthy such as those found in fish, nuts, and vegetable oils.
Moisture – Moisture-Associated Skin Damage(MASD) is skin breakdown caused by prolonged exposure to moisture such as urine, stool, sweat, wound drainage, saliva, or mucus. When exposed to excessive amounts of moisture, the skin will soften, swell, and become wrinkled, all of which make the skin more susceptible to damage.
How to Prevent Skin Tears
A prevention-oriented approach to skin care will lead health care practitioners to saving patient skin and avoid the cost of wound care on elderly patients:
Healthy Skin Inside and Out: Moisturizer is a simple way to keep skin flexible and healthy. A daily regime of rubbing lotion on arms and legs can prevent drying out and cracking skin. It is also important to hydrate. Dehydration is not only terrible for the skin, but for patient health all around. As mentioned above a diet rich in healthy fats such as nuts, tomatoes, spinach and fatty fish is food for the hypodermis .
Safety Measures: Skin tears are sometimes caused by bumping into your walls, chairs and corners. Take time not to stand up too fast, provide good lighting, and keep areas uncluttered to reduce the chances of accidents.
Educate Caregivers on Proper Dressing Removal: The removal of medical tape is often a source of skin tears in care facilities. Adhesive solvents dry out the skin. Remove tape carefully and slowly. Some patients have adverse reactions to skin prep as well making adhesives more aggressive.
Use Skin Friendly Adhesives: Hy-Tape is a proven leader in skin tear prevention. The latex free, zinc oxide based adhesive is nonreactive so patients with sensitive skin depend on Hy-Tape to keep skin healthy. Hy-Tape also has a reputation for holding firm, but because of the thermal reactive properties, it does not get more aggressive when body temperatures rise and therefore releases gently.
We ask that if you have an elderly patient, family member, or friend who has a wound or skin tear, that you try a sample of Hy-Tape. We also ask that you provide us with feedback on how the tape works.

